
Any low-rise residential building is constructed in such a way as to obtain a long service life and maximum usable space at the minimum cost of materials. From this point of view, attic spaces are of particular interest, allowing you to double the usable area without any additional changes. On the other hand, the construction of roofs whose rafter systems are designed to create a residential attic will be more complex.
Content
Types of roofs
Today, in the construction of country houses, several types of roofs are used:
- Slippery. This is the easiest option, since here you can often do without a ridge beam and even without a number of other elements that are mandatory in other cases. Typically, such solutions are used in the construction of utility rooms, outbuildings and garages, but they are also suitable for residential buildings with a small area.

Roofs of this type are among the most economical. They require a minimum amount of roofing material and wood, which is used for roof trusses.
- Gable. This is the second most difficult type of roof, since only two slopes are required here, and the rafter system, as a rule, is no different. Roofs of this type are one of the most popular in modern suburban construction, because, despite their simplicity, they cope well with wind and snow loads, and are also suitable for creating an attic.
- Four-slope. This category includes hip, tent and sloping roofs. In the latter case, it is worth mentioning that we are talking about a kind of gable roof, which received four slopes due to a break. Such structures are more complex than the two previous options, however, the aesthetics of the building along with them is higher.
- Gable and multi-slope. Sophisticated attachment points for rafters, special device technology and the need for careful calculation are the reasons why only professionals build such roofs. You can certainly try to build something yourself, of course, but only if you are an expert in this field.
The choice of roof type depends on the climate in the region and the wind load. The second point is the angle of inclination of the slopes, which depends on the location of the building, the presence of nearby arrays of buildings or trees and the climate.
Slope angle
An ideal option for any roof is a design that will require minimal attention from the owner. Self-cleaning roofs are generally attractive because they allow you not to worry about the accumulation of a large amount of snow.

The accumulation of snow can not be neglected, since its mass after intense snowfall can be up to 200 kg per m2, which means that only very strong rafters can withstand such a weight.
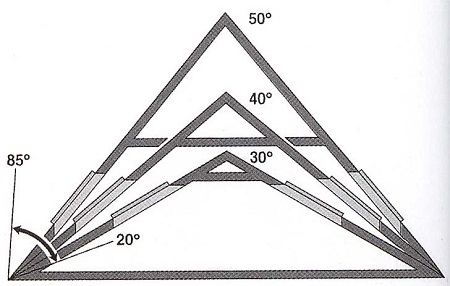
An alternative is the installation of an original roof like Alpine houses, with a very large slope of the slopes, often descending almost to the ground. It should be noted that to obtain the effect of removing snow will require an angle of 45 degrees. In this case, precipitation will roll over the coating under its own weight.
On the other hand, an increase in the slope of the slopes leads to an increased consumption of roofing and building materials.Moreover, if it is planned to build an attic, then the insulation will be expensive, because the higher the height of the ridge, the higher the consumption of this material. In addition to the cost of a pitched roof, its appearance also affects the choice of slope. For non-operated roofs it is not required to use a large amount of insulation, however, an increase in the angle of inclination does not always justify itself.

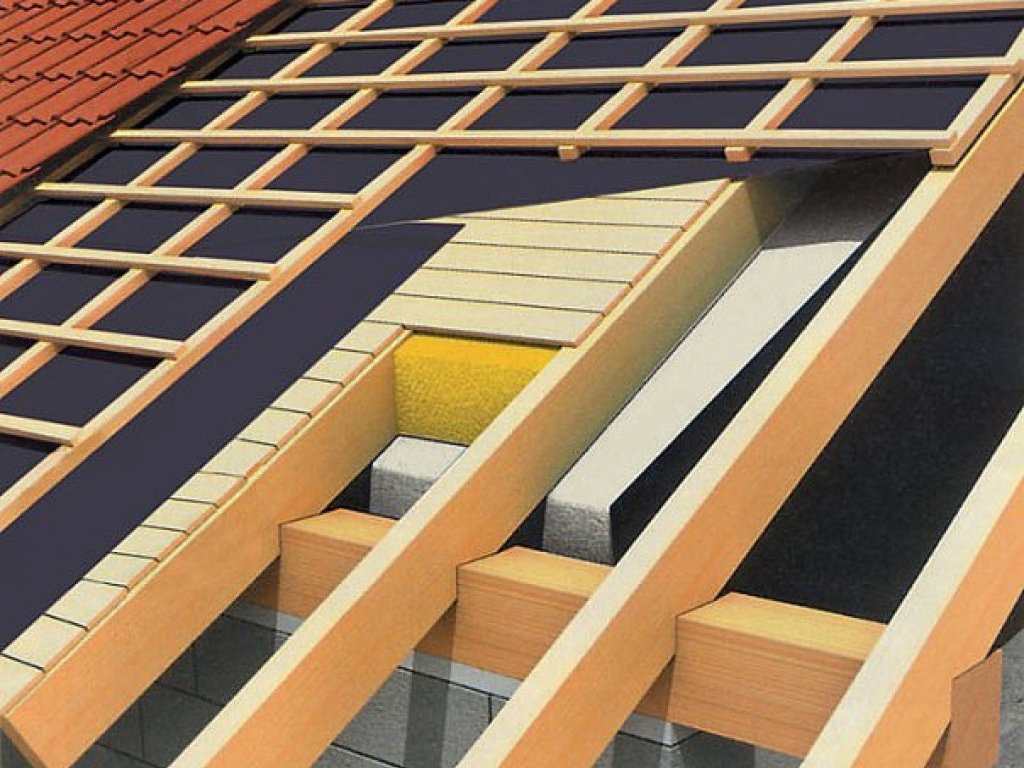
The main sign of an unexploited roof is another scheme of the rafter system and the absence of a gap between the ceiling and the external protective structure. Usually these are flat roofs or those that have a very small slope. Their main drawback is that during heavy snowfalls, snowdrifts can form, which will not only create a load on the ceiling, but also cause a "flood" during the thaw.
The type of roofing material will need to be determined in advance, since it must be taken into account when calculating the angle of the rafters. Typically, flexible materials and bituminous coatings are chosen for multi-plaster structures. For example, metal, corrugated board or galvanized iron. Other options, such as slate or tile, are better for roofs that have a simple configuration.

Classical tiles are rarely used today, because it requires a sufficiently large angle of inclination of slopes, ranging from 30 to 60 degrees.
Bituminous materials can be used even at small tilt angles (from 8 degrees), and the limit value for them is 18 degrees. Metal and asbestos cement sheets are used at angles from 14 to 60 degrees. We will not dwell on the consideration of roofing materials in detail, since this issue has already been highlighted on our website.
Spacer and non-supportive layered rafters
These are two types of rafters, one of which is chosen taking into account the shape of the house, the roof and the size of the future structure. Rafter rafters - this is an option suitable for single-pitched or double-pitched roofs. Their main feature is that they use two fulcrum. On the one hand, the rafter leg rests on the ridge of the roof, and on the other, on the wall of the house.
The non-piled layered rafters are mounted in such a way as to avoid bursting pressure on the wall of the house. Typically, roof truss structures are created using one of the following options:
- The rafter's foot rests on the Mauerlat. It is filed with a bar and fixed by cutting with a tooth. In addition, additional wire insurance is provided. The upper part of the timber is mounted on the ridge run. Fastening is carried out using the principle of a sliding support.
- The bottom of the rafter is attached through the use of a movable joint. As a mounting point, not only Mauerlat can be used, but also piece bars. The upper part is fixed with a bolt, nails or in another way after it is laid on the ridge run.
- The third option involves the installation of overhead rafters with a rigid mount to the run. Nails, studs or other hardware may be used here.

If the thickness of the rafters, which was originally selected, is insufficient, then during the work you can use supports that are mounted under too long elements in those places where maximum deflection is expected.

The roof rafters are spacer. In this case, it is supposed to create such a structure where bursting force will be transmitted to the walls of the house. The mounting method in this case is the same as in the previous one, however, the fastening of the rafter legs is fixed, so the whole system will receive internal stress. It is worth saying that this option is a transitional scheme that separates the undisputed layered rafters and hanging.
Hanging rafters
This design of the rafter system will be ideal when it is necessary to cover large spans, the length of which exceeds 7 m.In such a situation, there is only one fulcrum for the rafter leg - the wall. The upper part of the beam is connected to the oncoming element located on another slope. There are several options for joints: half-wood, slotted tenon, metal plates.
In order for the rafter legs to be securely fixed, it is necessary to connect them by tightening. Usually - this is a solid beam, which is attached to the bottom of these elements. Of course, it can be positioned even higher, but in this case the load will increase, which means that the weight of the beam will also need to be increased. In such a situation, one of the following mounting options for rafters can be used:
- The rafter leg is connected to the Mauerlat using an additional gash and is held securely with nails. The second option involves the use of metal corners. Then the upper parts of the rafters are joined end-to-end, and the lower parts are held by a puff. In this case, the top of the rafters can be pressed against the ridge run, which will rest on the headstock.
- Puffs are set so that the heels of the rafters abut with a chopped tooth against the edges of the puffs, which, in turn, are attached to the Mauerlat. The upper parts of the rafters are held with wooden lining.
- For the role of puffs, floor beams can be selected. In this case, their ends should be extended beyond the walls by at least 55 cm. Felling of the tooth nests is performed no closer than 25-40 cm from the edge of the wall.
- In houses made of logs, the fastening of the rafters is done on the upper crown through the thorn-socket connection. Special metal mounts, such as sliders, skids, etc., can also be used. The latter option will allow structural elements to move and avoid the occurrence of additional stresses.
The puffs themselves can be solid beams or components. Splicing of the bars is carried out in any convenient way, for example, with an oblique tooth, an overlap, etc. Puffs can be installed not only at the level of the heels of the rafters, but also in any other place.

If rafters for a roof are used, the dimensions of which are more than eight meters, then we recommend creating a structure from the headstock and struts, as well as using racks and crossbars that increase the reliability of the rafter system.
Rafters for different types of roofs

The simplest option is the construction of a shed roof, the rafters of which abut against the walls of the building. The length of these elements cannot exceed 4.5 meters, but there is also a solution for covering large areas. In this case, it is recommended to use supports or racks that will hold the long structure.
Most gable roofs are similar to each other as twins, but their internal structure can be very different. Today, four options are used:
- Apply a ridge run, on which the legs of the rafters rest. Slopes are enhanced by the use of truss legs, and the run is held upright. The racks themselves are installed on the bench. The width of this type of roof can reach 10 m.
- The second option involves the use of truss legs, the lower parts of which rest against the rack of the ridge run, and the upper parts in the scrum (tightening), connecting the rafter legs closer to the ridge. In this case, the width of the roof increases to 14 m.
- There is no ridge run. It is replaced by a beam located under one of the ramps. In addition, a tightening is used, rafter legs and a support resting on the supine. The angles of the rafters vary from 45 to 53 degrees. This option, compared with the previous one, does not give much gain in the width of the roof, however, it is suitable when the supporting wall is not located in the center of the building, but is shifted to the side.
- In the case when it is required to cover wide buildings, symmetrical structures can be used, using two runs, parallel to the rafters under the rafters. Such gable roofs involve the use of two puffs, the upper of which connects the rafters, and the lower - racks and rafters. The width of the structure in this case can reach 16 m.

The distance between the rafters is selected taking into account their length and section. For example, for a section of 40x150 mm, a step of 60 cm is necessary, for 50x150 - 90 cm, and for 100x150 - 215 cm.
The hip roof is another common option today that has worked well for country houses. It differs in that it does not have pediments, the place of which is occupied by additional slopes - hips. In the general case, the design assumes the presence of run, and conventional rafters on the main slopes and hip rafters on the side. Hip rafters are based on long diagonal elements, where they are joined with the upper parts of ordinary rafter legs. For such roofs, it is recommended to use reinforced piping.
A sloping roof completes the list, since it has a rather complicated structure. Here, a method is used that involves creating a frame for rafter legs, consisting of a horizontal beam and vertical racks, after which the remaining elements are installed. The upper crossbar of the U-shaped frame acts as an overlap of the attic, but the ridge of the skate also rests on it.

The distance between the rafters of the rafter system in this case should be chosen taking into account the load acting on the roof, the thickness of the beam used and the angle of inclination of the slopes.
The main issues regarding the installation of the rafter system for various types of roofs were discussed above, so this material can be used as a short guide, allowing you to quickly understand the issues of roof construction.





Alas, no comments yet. Be the first!