Thermal insulation of the roof, as well as attic and attic rooms is one of the most important and necessary stages of home improvement. And now we will try to understand what exactly the process of insulation of the roof consists of and what are the reasons for its necessity.
The constant positive temperature in the house and the attic depends directly on the thermal insulation of the enclosing structures - attic floors, external walls - as well as on the insulation of the roof, roof, attic. Such measures contribute to the formation of a comfortable microclimate in the rooms of the house and increase the chances of effective energy saving.

A competent approach to the process of thermal insulation of a pitched roof will provide you with additional conditions for transforming an attic into an attic. Thus, another advantage will appear - the expansion of the used area in the house.
When repairing a building, at the same time, energy consumption can be reduced by additionally warming the walls, roof and facade. Moreover, based on new building standards, the requirements regarding the thermal resistance of walls and ceilings have increased significantly. Therefore, during construction from scratch, during reconstruction and modernization, as well as during overhaul, the implementation of thermal insulation is impossible without the use of effective materials.
Content
Criteria for the selection of thermal insulation materials
The durability and stability of the thermophysical, as well as physico-mechanical properties that are part of the design of the fencing of the insulating material for the roof depends on the influence of various factors. They must be taken into account when choosing one or another material.
It should be attributed to such factors:
- geographical location of the house or building;
- change in humidity and temperature depending on the season (winter-summer);
- diffusion wetting of the roof and walls;
- capillary moistening of the roof and walls;
- mechanical stress;
- the impact of wind and snow loads (their degree depends on the angle of the roof).

Please note that the technological features of the installation of flat roofs are significantly different from the features of the installation technology of pitched roofs.
This applies directly to the roof insulation itself. Therefore, the choice of thermal insulation for a roof depends not only on the properties of the thermal insulation material, but also on the type of roof itself.
Thermal insulation materials vary in their composition, density, as well as in the coefficient of thermal conductivity, which expresses the average value of the heat loss of the insulation (1 sq. M per unit time). Increased requirements for roof insulation are also associated with increasing humidity and temperature differences, which lead to an increase in heat loss of the material. Physico-technical qualities, in turn, affect the operational reliability of the design and thermal performance.
Roof insulation functions
In addition to the above, the roof insulation is responsible for such functions:
- Reduces the influence of temperature fluctuations on most of the roofing. This creates protection against cracking, which threatens the unevenness of temperature differences.
- It transfers the center of condensation formation to the outer layer of thermal insulation.Thanks to this feature, a concrete or reinforced concrete roofing does not damp.
- In addition to roofing, thermal insulation protects against air vibrations from outside the room in the house.
- Affects a decrease in temperature differences in indoor air, as well as the ceiling surface (even in the attic).
- It forms a favorable microclimate, increasing the temperature of the interior of the ceiling.
- In cold weather it prevents the formation of condensation in the "pie" of the roof. This is especially important for rooms of some kind, for example, warehouses.
Thermal insulation for flat roofs: roll insulationmi and masticmi materialami
For insulation of a flat roof, the following materials are used:
- Styrofoam
- extruded insulation
- hard (from mineral wool).
Each of them has certain qualities that serve as a selection criterion for different types of flat roofs.
For example, foam insulation is used for non-operating roofs, and only if the composition of their roofing "pies" contains a fireproof pillow that protects the insulation.
What is called a fireproof pillow? It can be a screed (on top of the insulation) and reinforced concrete floor (bottom of the insulation).
As for extruded insulation, it is applicable for coatings on inverse roofs (exploited inverted) and on loaded roofs.
On lightweight structures and flat non-exploitable roofs with screeds, mineral wool insulation (hard) is used.
The type of roof, as already mentioned, greatly affects the installation method of the insulation, because there are several options for the installation of the insulation.
Lightweight roofs require one approach to the device, loaded ones require another, and ordinary roofs require a completely third. And this must be remembered.
Pitched roofs and their insulation
There are various scenarios in which attic and attic rooms are insulated. This is due to the fact that premises of this kind are fundamentally different in their structure. There are also differences in the technology of installation of roofs. So, the roof in the attic is insulated along the slope itself, and in the attic - the insulation is laid between the lags in the ceiling, on top of the ceiling.
When planning to use the attic as an additional, but non-residential room, when laying the insulation, you need to know that the insulation layer must be hidden under the wooden flooring from the boards.

Please note - if the insulation layer is not protected by the flooring from the boards, then during operation of the room the roof insulation can be significantly damaged!
If the attic is rarely visited, for example, in the case of a check, then to protect the thermal insulation layer from damage, it will be possible to do with the flooring of pedestrian gangways.
A full living room in the attic will require more effort, but it will also give more opportunities in terms of expanding the useful area of the house. Here you will need to make an effort - to arrange an attic.
Installation of attic thermal insulation
When arranging the attic, first of all, you need to build a roof ventilation system. At the same time, observe all the rules of the technology of installation of roof insulation. And it is here that various difficulties and mistakes can lie in wait for you.

If you are not sure of the correctness of your actions, then it is better to resort to the advice of professional builders, otherwise the wrong installation technology can lead to complete roof dismantling and replacement of insulation!

If we compare the installation of the attic and the installation of the attic, then with the thermal insulation of the last insulation you will need a couple more cubes. Accordingly, the boards will also leave more. And, most importantly, do not forget about installing a vapor barrier and waterproofing, since the first one can prevent the insulation layer from getting wet (due to the penetration of moisture vapor), and the second one will protect the roof insulation from condensation that forms on the inside of the roof covering.
Remember that the attic and attic are arranged under a pitched roof, which requires the use of a certain type of insulation with appropriate physical and technical qualities. Insulators for such purposes are of low and medium hardness, and their density is from 35 to 125 kilograms per cubic meter.
Typically, for pitched roofs, heaters with a mineral or fiberglass base are selected. Glass wool insulation is fraught with large heat losses, since their main quality is high thermal conductivity. But with all this, glassy material is financially profitable.
And mineral wool insulation is characterized by a low percentage of environmental friendliness.
Vapor barrier problems arising from roof insulation
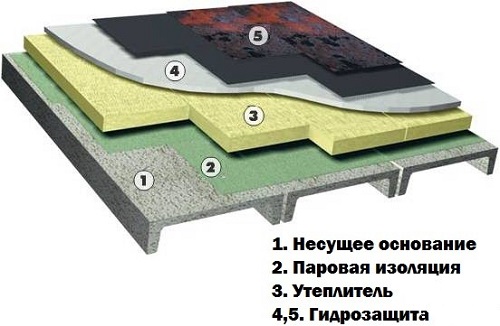
The classic thermal insulation of the roof in the form of a pie has the following scheme:
- Vapor barrier.
- Thermal insulation.
- Water and moisture protection.
In Soviet times, glassine was used for vapor barrier purposes, mineral wool was used for thermal insulation, but waterproofing was neglected or, in extreme cases, roofing material or the same glassine were used.
Today, glassine has been replaced by vapor barrier membranes - polyethylene films (characteristics 22mg / m2 / day). Mineral wool has given way to expanded polystyrene (regular or extruded) and today it is losing demand, and perforated polyethylene (characteristics - 1000 mg / m2 per day) successfully serves as wind and moisture protection of the roofing “cake”.
Almost all country houses have this kind. Of course, many buildings are well equipped and able to cope with winter cold. But still, most houses cannot adequately endure the winter, and the owners are forced to put up with either huge energy costs, or with cold and severe frosts, or even leave the house for winter time.
It’s even more annoying that after winter colds and snow, when everything seemed to be behind us, the thaw sets in and brings with it a new serious problem - the roof leakage.
But in fact, the problem is not in the course of the roof, but in another. In what? In order to comply with the order, we will consider the functions that lie on each part of the heat-insulating “pie” of the roof.
What is vapor barrier: main functions
The need for vapor barrier is associated with preventing the penetration of steam into the region of the layers of thermal insulation. What for? Imagine that there is no vapor barrier.
For a detailed interpretation, we need to go a little deeper into physics. So, a molecule of water or steam has a very small size, but a high level of kinetic energy. Therefore, it can pass through any material, except for such as glass, metal and water itself. Even vapor barrier films made of special high-quality polyethylene will still allow steam to pass through (22 mg through 1 m2 per day). In addition, the desire of steam to leak through the roof is associated with a huge accumulation of molecules in the space under the roof. Simply put, the warm air in a room cannot but move up.

Such a process suggests that the steam that comes out of the house seeps through mineral wool and cracks at the joints of polystyrene plates or through cracks in the roof surface. In such cases, the temperature drops sharply, and the vapor molecule first forms frost and then a layer of ice. Subsequently, it fills all the cracks or, if any, mineral wool, which refers to open-porous materials. The ice builds up over time and, accordingly, the insulation performance of the insulation deteriorates, and in the case of mineral wool they disappear altogether, which makes it completely unsuitable.
So, vapor barrier is needed in order for the heat-insulating material to perform its functions qualitatively.
As for thermal insulation, we have already spoken about this in detail above.
But wind and moisture protection, consisting of a film material, includes three functions that are performed to protect thermal insulation:
- increasing the characteristics of the insulation due to moisture protection;
- wind protection;
- steam outlet.
Exactly the same vapor that nevertheless seeped through the vapor barrier membrane. This is the essence of perforated material: holes are so small that rain and wind are not able to pass through them, but steam can pass fifty times better than through a vapor barrier film. It is this difference that can ensure a uniform steam output at a temperature difference of 50 degrees Celsius.
So, having understood all the features of roof insulation, we came to the conclusion that the main thing in this process is to choose the right material, observe all the rules for installing insulation, taking into account the type of building roof (pitched, flat), and also, in the case of a pitched roof, determine Will the attic room be exploited and how much. Choosing the right approach and knowing the nuances of installation (do not forget about vapor barrier and moisture protection!), You can insulate the roof of your house perfectly!





Alas, no comments yet. Be the first!