
To draw up a technical design of the house, the calculation of rafters is necessary. There are several options for roof structures.
Rafter legs, which are supported by two supports, while they do not have any additional stops, are called rafters without braces. They are used for single-pitched roofs, the span of which is about 4.5 meters or for gable roofs, whose span is about 9 meters. The rafter system is used either with the transfer of the thrust load to the Mauerlat, or without transmission.
Content
Rafters without races
The rafter working on a bend, not transferring the load on the walls, has one support firmly fixed and freely rotating. The other support is movable and rotates freely. Three options for attaching rafters can meet these conditions. Consider in detail each.
- The bottom of the rafter is hemmed with a support bar, or a cut is made on it with a gash. It is the cutting rafter that abuts the Mauerlat. In the upper part of the rafters, an enlarged horizontal notch with a bevel is performed. The dimensions of the cut in the upper part of the rafters are calculated as follows: a = 0.25. That is, the cutting length is performed no more than the height of the rafter section.
Trimming is recommended to be mowed to remove obstacles for bending the rafters. Otherwise, the cutting will abut the run. The result is a spacer system for the rafters. The length of the beveled trim must be at least two values, that is, at least two depths. In the case when it is impossible to trim the top of the rafters. It should be hemmed with a bar, using mounting brackets, double-sided plates or timbers made of wood. The upper edges of the rafters are freely laid on the run. In gable roofs, they are mounted on girders, like a sliding support beam, but they are not fastened together. In this case, a gable roof is considered as two gable roofs that adjoin each other with high sides.

The binder of the top of the rafter leg or the upper support cut is installed in a horizontal position. It is enough just to change the method of bearing on the run, and the rafter leg will immediately show the spacer. This calculation of the rafter legs, due to the harsh conditions for creating the upper node, is usually not used for gable roof options. Most often it is used in the construction of single-pitched roofs, since the slightest inaccuracy in the manufacture of the unit will turn the circuit uncontested into a spacer. In addition, in gable roof types, in the event that there is no strut on the Mauerlat, due to the deflection of the rafters under the action of the load, destruction of the roof ridge assembly may occur.
At first glance, this system may seem unrealistic in execution. Since the lower part of the rafters is emphasized in the Mauerlat, in fact, the system should exert pressure on it, that is, horizontal force. However, she does not show the spacer load.
-
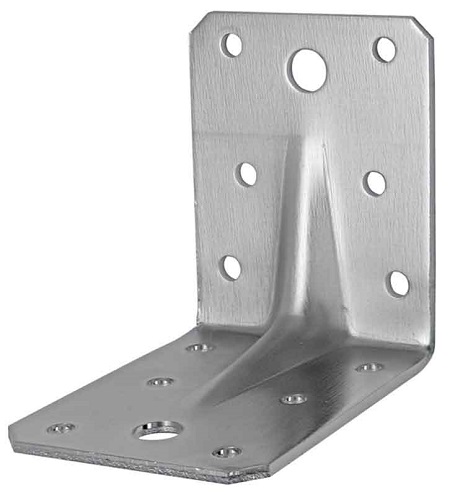

Angles for fixing rafters The second option for attaching rafters is the most common installation method related to gable roofs. In this case, the bottom of the rafters is made on a slider, the top is fixed by connecting it with nails or bolts, or resting against each other or in the run. They are connected either with metal plates with teeth, or with wooden tricks.
It is necessary to pay special attention to the fastening of the rafters to the Mauerlat.This action comes down to fixing the rafter legs in a position that will provide the installation step. To do this, drive one long nail on both sides of the element, and fix the structure on top with a steel plate with teeth. If you fasten the rafters with the help of metal corners, then for securely fixing the rafter leg, one nail will be enough, or you can press the rafter leg with corners on both sides without nails.
When fixing the rafter legs with metal plates with spikes, there is no need to hammer as many nails as there are holes in the corner. Otherwise, the slider will become an imperfect hinge, and the Mauerlat will become a spree.
Durable wires hold the roof from tipping under the wind. Do not neglect these roof elements and shift their function to the corners. Otherwise, the rafter system should be erected as a spacer.
- Raspor does not give hard pinching of the ridge node, in the case when the bottom of the rafters is done on a slider, and the top is fixed in a rigid way. Otherwise, a bending moment may appear in the ridge node, which will tend to destroy it. In this design, the maximum bending moment will occur on the ridge support, and the rafters will receive less deflection.
It should be borne in mind that using this ridge node, a sufficiently large bearing capacity of the rafter system will be obtained. Simply put. If you use a nodal connection in construction with a rigid connection of the top of the rafters, even if you do not calculate the ridge node mathematically, you will get some margin of sufficient strength on the rafters.
Thus, in all three cases, the following rule is observed: one edge of the rafter is mounted on a sliding support, which allows you to make a turn. Another on the hinge, which allows only a turn. The fastening of the rafter legs on the sliders are installed using a variety of designs. Most often, they are performed using mounting plates. It is also not excluded and fastening with nails, self-tapping screws, using overhead bars and boards. It is only necessary to correctly choose the type of fastener that will prevent the rafter from sliding in the support.
How to calculate the rafters
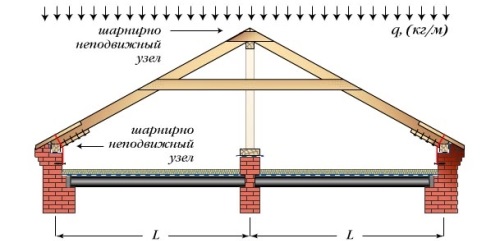
In the process of calculating the rafter structure, as a rule, an “idealized” calculation scheme is adopted. Based on the fact that a certain uniform load will be pressed on the roof, that is, an equal and equal force that acts uniformly along the planes of the ramps. In reality, there is no uniform load on all roof slopes. So, the wind sweeps snow onto some slopes and blows off from others, the sun melts from some slopes and does not reach the others, the same situation with landslides. All this makes the load on the slopes completely uneven, although outwardly this may not be noticeable. However, even with an unevenly distributed load, all three of the above options for rafter mounts will remain statically stable, but only under one condition - a rigid connection of the ridge run. At the same time, the run is either propped up with slanting rafter legs, or introduced into the gables of the wall panels of the hip roofs. That is, the rafter structure will remain stable only if the run of the ridge is firmly fixed from a possible horizontal displacement.
In the case of the manufacture of a gable roof and support of the run only on racks, without support on the walls of the fronts, the situation worsens. In variants numbered 2 and 3, when the load on a slope decreases, in contrast to the calculation on the opposite slope, the roof may move in the direction where the load is greater.The very first option, when the very bottom of the rafter leg is made with a notch with teeth or with a hem of the support bar, while the top of the horizontal knuckle is laid on the run, it will hold the uneven load well, but only if the racks that hold the ridge run are perfectly vertical.
In order to give the rafters stability, a horizontal bout is included in the system. It is insignificant, but still increases stability. That is why in those places where the scrum intersects with the stances, it is fixed with a nail battle. The statement that the fight always works only in tension is fundamentally wrong. Scrum is a multifunctional element. So, in a non-rafter rafter structure, it does not work in the absence of snow on the roof, or only works on compression, when a slight uniform load appears on the slopes. Tensile construction works only when the subsidence or deflection of the ridge run under maximum load. Thus, the scrum is an emergency element of the rafter structure, which comes into operation when the roof is littered with a lot of snow, the ridge run will be bent to the maximum calculated value, or uneven unforeseen subsidence of the foundation will occur. The result may be an uneven subsidence of the ridge run and walls. Thus, the lower the contractions are set, the better. As a rule, they are installed at such a height that they would not create obstacles when walking in the attic, that is, at an altitude of about 2 meters.

If in options 2 and 3 the lower node of the support of the rafters is replaced with a slider with the extension of the edge of the rafter leg behind the wall, this will strengthen the structure and make it statically stable with completely different combinations of the structure.
Also, one good way to increase the stability of the structure is to firmly fasten the bottom of the racks, which will support the run. They are installed by cutting into the bed and fixed with overlapping by any available means. Thus, the lower node of the pillar support is transformed from a hinge to a node with rigid pinching.

How to calculate the length of the rafters does not depend on the method of attaching the rafter legs.
The section of contractions, due to the development of fairly small stresses in them, is not taken into account in the rafters, but is accepted rather constructively. In order to reduce the size of the elements that are used in the process of constructing the truss structure, the cross section of the scrum is the same size as the truss leg, and thinner discs can be used. Fights are set either on one or on both sides of the rafters and fastened with bolts or nails. When calculating the cross section of the rafter structure, contractions are not taken into account at all, as if they were not at all. The only exception is bolting the contractions to the rafters. In this case, the bearing capacity of the wood, due to the weakening of the bolt hole, is reduced by using the coefficient of 0.8. Simply put, if holes in the rafters are drilled to install bolt contractions, then the calculated resistance must be taken in the amount of 0.8. When fixing fights on rafters only with a nail battle, weakening of the resistance of the rafter tree does not occur.
But it is necessary to calculate the number of nails. The calculation is made for the cut, that is, the bending of nails. For the calculated force, they take the strut that occurs in the emergency situation of the rafter structure. Simply put, in the calculation of the connection between the nails of the scrum and the rafter leg, a spacer is introduced, which is absent during the standard operation of the rafter system.

The static instability of the rafters without a support system is manifested only on those roofs where it is not possible to install a ridge run that protects against horizontal displacement.
In buildings with hip types of roofs and pediments made of stone or brick, rafter systems without rafters are stable enough and there is no need to take measures to ensure greater stability. However, to counter the emergency of constructions, contractions should still be established. When installing bolts or studs as fasteners, you should pay attention to the diameter of the holes for them. It should be the same with the diameter of the bolts or slightly smaller. In the event of an emergency, the scrum will not work until a gap between the hole wall and the stud is selected.
Please note that in this process, the bottoms of the rafters will corrode to a distance of several millimeters to several centimeters. This can lead to a shift and scrolling of the Mauerlat and to the destruction of the cornice of the walls. In the case of expansion rafter systems, when the Mauerlat is firmly fixed, this process can cause the walls to move apart.
Expansion rafters
A rafter that performs bending work and transfers the thrust load to the wall panels must have at least two fixed supports.
To calculate this type of rafter systems, in the previous schemes we replace the lower supports with different degrees of freedom with supports with a single degree of freedom - articulated. To do this, where there are none, bars for support are nailed to the edges of the rafter legs. As a rule, a bar is used, the length of which is not less than a meter, and the cross section is about 5 by 5 cm, taking into account the nail connection. In another embodiment, you can arrange support in the form of a tooth. In the first version of the calculation scheme, when the rafters rest horizontally in the run, the upper ends of the rafters are sewn with either nails or a bolt. Thus, the articulated support is obtained.
As a result, the design schemes practically do not change. The internal stresses of bending and compression remain unchanged. However, a spacer force appears in the former supports. In the upper nodes of each rafter leg, an oppositely directed spacer disappears from the end of the other rafter leg. Thus, it does not cause much trouble.

The edges of the rafters, which abut against each other or through the run, may be checked for crushing of the material.
In rafter spacer systems, the purpose of the fight is different - in emergency situations it works for compression. In the process, it reduces the spacer on the walls of the edge of the rafters, but does not completely exclude it. She will be able to completely remove it if she fixes herself at the very bottom, between the edges of the rafter legs.
We draw your attention to the fact that the use of expansion roof truss structures requires careful consideration of the effect of the thrust force on the walls. It is possible to reduce this spacer by installing hard and durable skating runs. It is necessary to try to increase the rigidity of the run by installing racks, cantilever beams or struts, or to erect a construction hoist. This is especially true for houses made of timber, chopped logs, lightweight concrete. Concrete, brick and panel houses are much easier to carry the force of thrust on the walls.
Thus, the rafter structure, built according to the spacer version, is statically stable under various combinations of loads, it does not require rigid mounting of the Mauerlat to the wall. In order to hold the spacer, the walls of the building must be massive, equipped with a monolithic reinforced concrete belt around the perimeter of the house. In the event of an emergency, inside the spacer system that works for compression, the scrum will not save the position, but only partially reduce the spacing that is transmitted to the walls. In order to prevent an emergency, it is necessary to take into account all the loads that can act on the roof.
Thus, no matter what shape the roof of the house is chosen, the entire rafter system must be calculated in such a way as to satisfy the provisions of reliability and strength.To make a complete analysis of the rafter structure is not an easy task. In the calculation of wooden rafters, it is necessary to include a large number of different parameters, including strut, bending, possible weight loads. For a more reliable arrangement of the rafter system, it is possible to install more suitable methods of fastening. In this case, one should not take the dimensions of the rafters without having made a complete analysis of their technical and functional abilities.
Calculation of the cross section of rafters
The cross-section of the rafter beams is selected taking into account their lengths and the received load.
So, a bar up to 3 meters long is selected with a cross-sectional diameter of 10 cm.
A beam, up to 5 meters long, - with a diameter of 20 cm.
A beam, up to 7 meters long - with a cross-section diameter of up to 24 cm.
How to calculate rafters - an example
Dan is a two-story house measuring 8 by 10 meters, the height of each floor is 3 meters. Roofing selected corrugated asbestos-cement sheets. The roof is gable, the supporting posts of which are located on the central load-bearing wall. Rafter pitch 100 cm. You need to choose the length of the rafters.
How to calculate the length of the rafters? In the following way: the length of the rafter legs can be selected so that they would lay three rows of slate sheets on them. Then the required length: 1.65 x3 = 4.95 m. The roof slope in this case will be equal to 27.3 °, the height of the formed triangle, that is, the attic space, 2.26 meters.





Alas, no comments yet. Be the first!